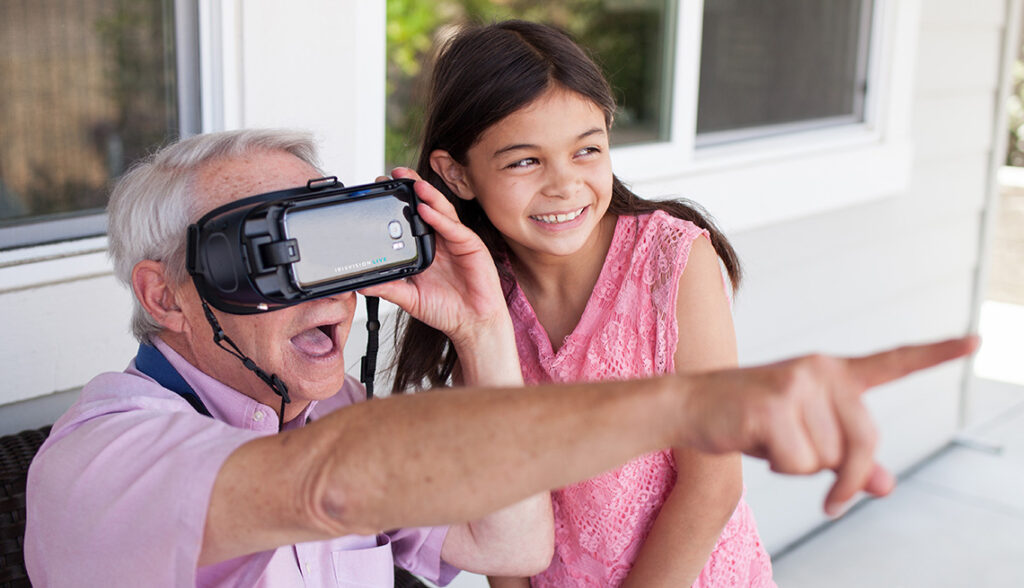
Low vision rehabilitation is a specialized service designed to help individuals with significant vision loss that cannot be fully corrected with glasses, contact lenses, medication, or surgery. The goal of low vision rehabilitation is to maximize the remaining vision and improve the quality of life by teaching adaptive techniques, providing assistive devices, and offering emotional support.
Key Components of Low Vision Rehabilitation:
Comprehensive Assessment:
- A low vision specialist evaluates the patient’s visual acuity, visual field, and functional vision.
- The assessment helps identify specific challenges and goals for rehabilitation.
Individualized Rehabilitation Plan:
- Based on the assessment, a personalized plan is created to address the patient’s unique needs and lifestyle.
- The plan may include training, assistive devices, and strategies to perform daily activities.
Assistive Devices and Technology:
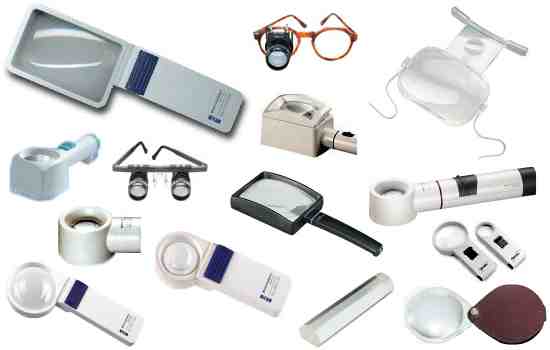
- Optical Devices: Magnifiers, telescopic lenses, and special glasses to enhance vision.
- Non-Optical Devices: Large-print books, high-contrast materials, and tactile markers.
- Electronic Aids: Screen readers, text-to-speech software, and video magnifiers (CCTVs).
- Lighting Adjustments: Proper lighting to reduce glare and improve visibility.
Training and Skills Development:
- Orientation and Mobility Training: Techniques to navigate safely indoors and outdoors, often with the use of a white cane or guide dog.
- Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Training: Strategies to perform tasks like cooking, reading, and personal care independently.
- Visual Skills Training: Exercises to improve the use of remaining vision, such as scanning and tracking.
Emotional and Psychological Support:
- Counseling and support groups to help patients cope with the emotional impact of vision loss.
- Encouragement to maintain social connections and engage in meaningful activities.
Collaboration with Other Professionals:
- Low vision rehabilitation often involves a team of professionals, including ophthalmologists, occupational therapists, and social workers, to provide comprehensive care.
Conditions That May Benefit from Low Vision Rehabilitation:
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
- Glaucoma
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Retinitis pigmentosa
- Stargardt disease
- Cataracts
- Other conditions causing irreversible vision loss
Goals of Low Vision Rehabilitation:
- Enhance independence and safety in daily life.
- Improve the ability to perform tasks such as reading, writing, and using technology.
- Boost confidence and emotional well-being.
- Provide tools and strategies to adapt to vision loss.
How to Access Low Vision Rehabilitation:
- Consult an ophthalmologist or optometrist specializing in low vision.
- Seek referrals to low vision clinics or rehabilitation centers.
- Explore resources from organizations like the American Foundation for the Blind (AFB) or the National Federation of the Blind (NFB).
Low vision rehabilitation empowers individuals with vision loss to lead fulfilling lives by leveraging their remaining vision and adopting adaptive strategies. If you or someone you know is experiencing significant vision loss, consider reaching out to a low vision specialist to explore rehabilitation options.